
(* equal contribution)
International Journal of Robotics Research (IJRR), 2022.
Abstract
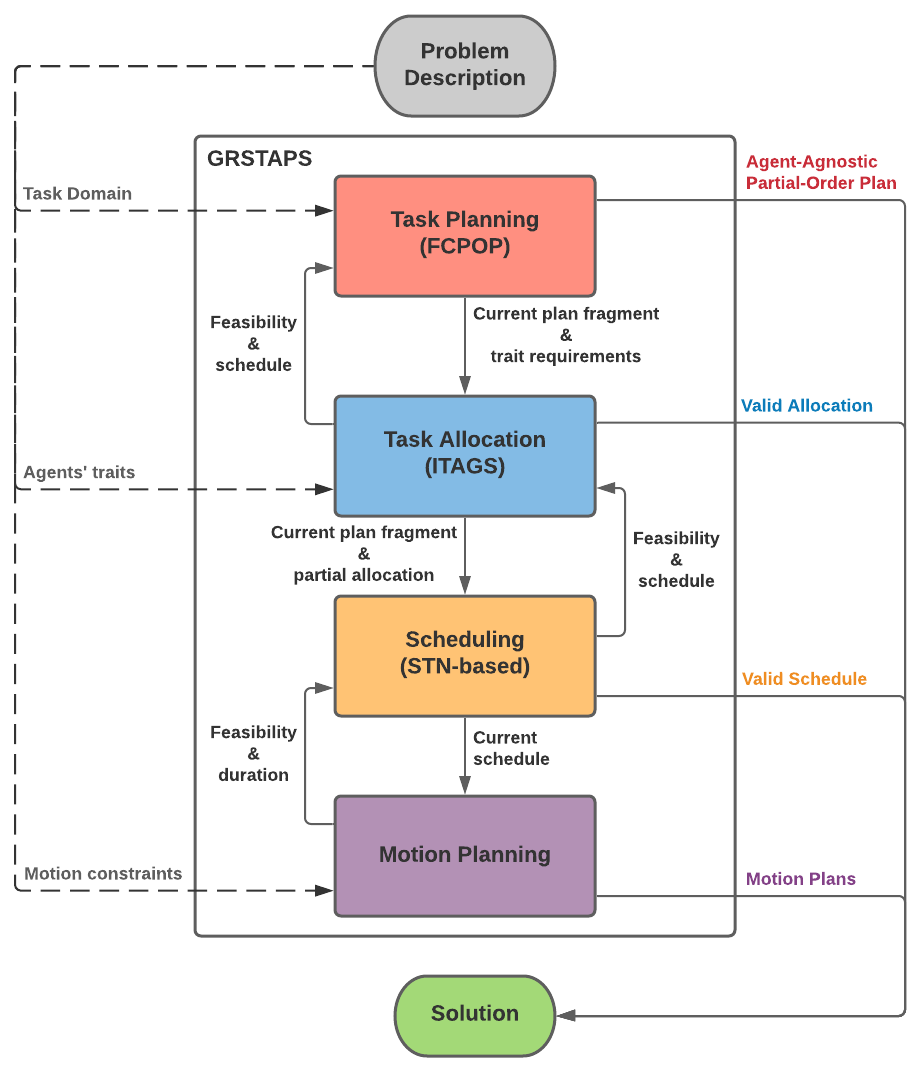
Effective deployment of multi-robot teams requires solving several interdependent problems at varying levels of abstraction. Specifically, heterogeneous multi-robot systems must answer four important questions: what (task planning), how (motion planning), who (task allocation), and when (scheduling). While there are rich bodies of work dedicated to various combinations of these questions, a fully integrated treatment of all four questions lies beyond the scope of the current literature, which lacks even a formal description of the complete problem. In this paper, we address this absence, first by formalizing this class of multi-robot problems under the banner Simultaneous Task Allocation and Planning with Spatiotemporal Constraints (STAP-STC), and then by proposing a solution that we call Graphically-recursive simultaneous task allocation, planning, and scheduling (GRSTAPS). GRSTAPS interleaves task planning, task allocation, scheduling, and motion planning, performing a multi-layer search while effectively sharing information among system modules. In addition to providing a unified solution to STAP-STC problems, GRSTAPS includes individual innovations both in task planning and task allocation. At the task planning level, our interleaved approach allows the planner to abstract away which agents will perform a task using an approach that we refer to as agent-agnostic planning. At the task allocation level, we contribute a search-based algorithm that can simultaneously satisfy planning constraints and task requirements while optimizing the associated schedule. We demonstrate the efficacy of GRSTAPS using detailed ablative and comparative experiments in a simulated emergency-response domain. Results of these experiments conclusively demonstrate that GRSTAPS outperforms both ablative baselines and state-of-the-art temporal planners in terms of computation time, solution quality, and problem coverage.