
IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), 2022.
Abstract
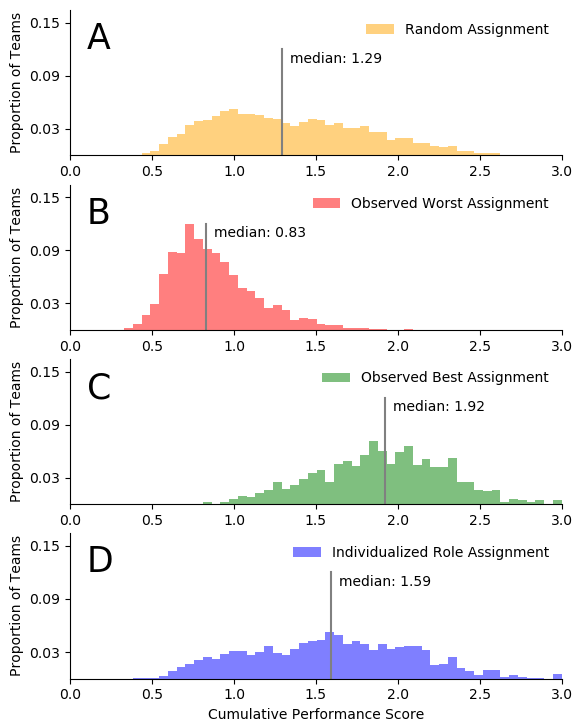
Mixed human-robot teams (HRTs) have the potential to perform complex tasks by leveraging diverse and complementary capabilities within the team. However, assigning humans to operator roles in HRTs is challenging due the significant variation in user capabilities. While much of prior work in role assignment treats humans as interchangeable (either generally or within a category), we investigate the utility of personalized models of operator capabilities based in relevant human factors in an effort to improve overall team performance. We call this approach individualized role assignment (IRA) and provide a formal definition. A key challenge for IRA is associated with the fact that factors that affect human performance are not static (e.g., fatigue and workload are known to significantly affect performance in HRT tasks). Instead of relying on time- consuming and highly-intrusive measurements taken during the execution of tasks, we propose the use of short cognitive tests, taken before engaging in human-robot tasks, and predictive models of individual performance to perform IRA. Results from a comprehensive user study conclusively demonstrate that IRA leads to significantly better team performance than a baseline method that assumes human operators are interchangeable, even when we control for the influence of the robots’ performance. Further, our results point to the possibility that such relative benefits of IRA will increase as the number of operators (i.e., choices) increase for a fixed number of tasks.